Rectangular Section - Torsional Loading
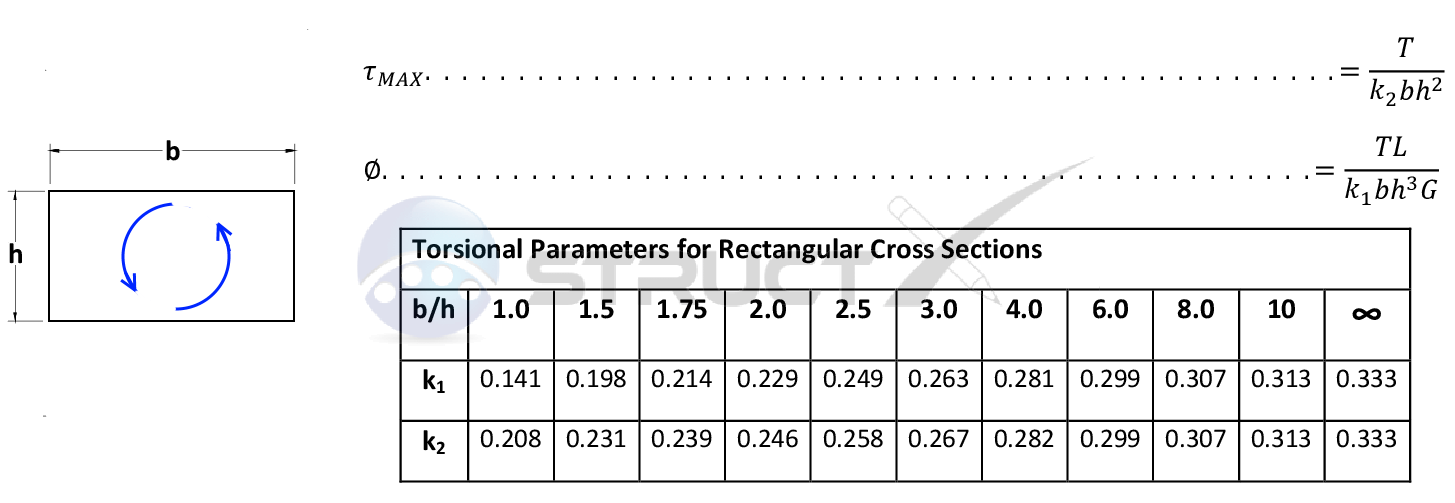
Notation and Units
Metric and Imperial Units
The above formulas may be used with both imperial and metric units. As with all calculations care must be taken to keep consistent units throughout with examples of units which should be adopted listed below:
Notation
- L = length under consideration, in or mm
- G = shear modulus or modulus of rigidity, psi or MPa
- k = torsional parameters, unitless
- T = applied or resulting torsion, lb.in or Nmm
- θ = angle of twist, degrees
- τ = shear stress, psi or MPa
Additional Resources
- A.C. Ugural, S.K. Fenster. Advanced Strength and Applied Elasticity. Elsevier, USA. 1975. Print.
- A.F. Hughes, D.C. Iles, A.S. Malik. Design of Steel Beams in Torsion. UK. 2011. Print.
- G.E. Maddux, Air Force Flight Dynamics Laboratory. Strees Analysis Manual. U.S. 1970. Print.
- H.M. Montrey, E.W. Kuenzi. Design Parameters for Torsion of Sandwich Strips Having Trapezoidal, Rectangular and Triangular Cross Sections. Madison, Wisconsin. 1972. Research paper.
- University of Florida, Department of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering. (n.d.). Narrow rectangular cross section [PDF PowerPoint file]. Retrieved from http://www2.mae.ufl.edu/haftka/adv-elast/lectures/sections6.5-6.pdf
